Conceptually, social commerce isn’t new — it has existed in some form ever since people have made recommendations to each other. Today social networks are more powerful than ever, and startups and corporations are innovating new commerce models that leverage the greater reach available to us.
It’s important to understand the blurry, yet persistent difference between social commerce and conventional e-commerce. Where e-commerce aims for a direct, digital translation of brick-and-mortar browsing, social commerce refocuses the entire customer journey to center on people.
Social commerce doesn’t silo our retail experiences from the rest of our lives; rather it leverages the power of community and connection to create opportunities in everyday life through social networks.
Globally, social commerce is on the path to becoming a $1.2 trillion industry by 2025, with the biggest gains being made in Brazil and India. The $2 billion to $3 billion social commerce market in India today is estimated to hit $70 billion in value by 2030, empowering around 40 million small entrepreneurs.
However, the true growth story of social commerce is in Southeast Asia, where it is already worth more than $13 billion.
Using social commerce to foster communal growth
The popularity of social commerce in Southeast Asia has been accelerated by high rates of mobile internet penetration, a mobile-first generation that spends a lot of time on social media, and high engagement.
But the biggest driver of social commerce is the fact that this is a collectivist society. At the heart of Southeast Asian culture and approach to life is a community that is interwoven into the fabric of everyday life. While Southeast Asians feel confident they can succeed as individuals, they still appreciate the value of their traditionally collectivist society.
Image Credits: Kantar Global MONITOR 2019
Southeast Asians have a strong desire to belong in a community, and finding strong relationships is more important to them than their global counterparts. They use their networks for socializing as well as transacting, and they’re particularly enthusiastic about peer-to-peer services.
And this sense of communal belonging affects the way they buy.
The social commerce model leverages community leaders and influencers’ connections to generate sales by marketing directly to their friends and family. Through social platforms or a platform app, these leaders, acting as resellers, can order products at wholesale prices before redistributing to their networks at a markup; though in some cases, they may also earn a percentage commission.
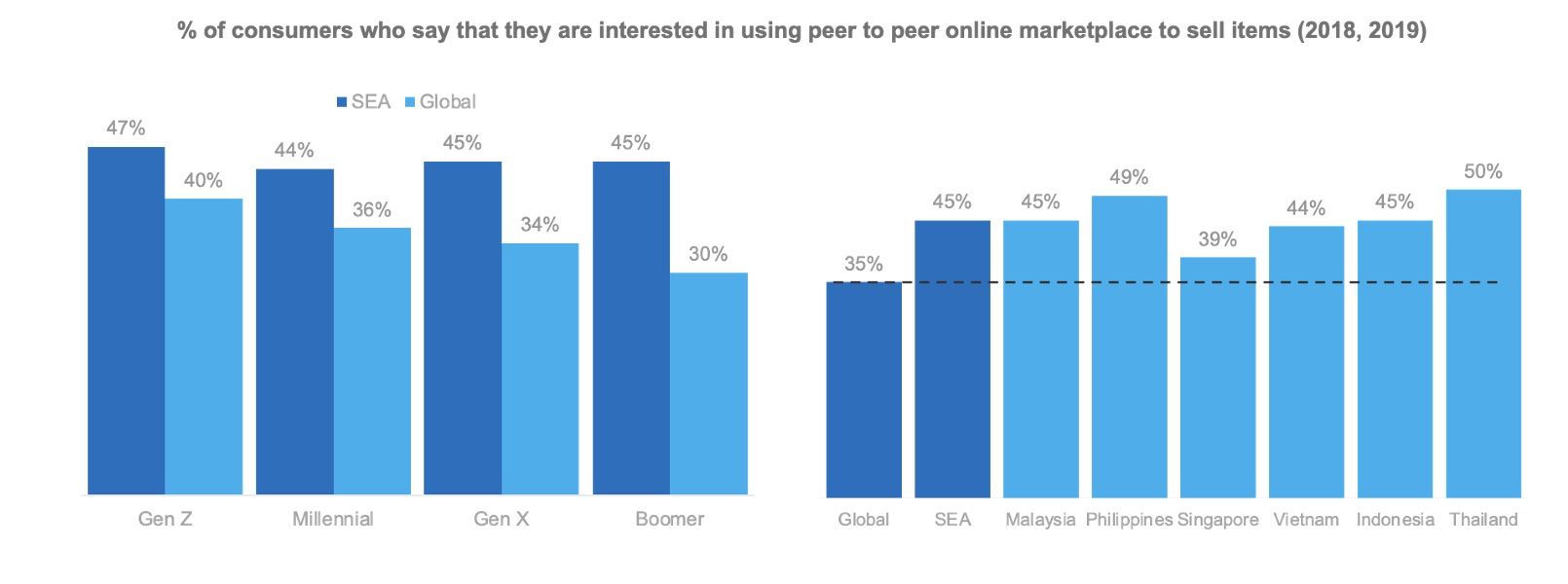
Image Credits: Kantar Global MONITOR 2019
Addressing logistics issues in tier 2 and tier 3 cities
Source : How social commerce is bridging Southeast Asia’s infrastructure gaps











